Array不是一般意义上的“容器”
讲容器之前,请允许我先把Array和其他所有的容器区分开来。它是Java语言内置(compiler-supported type)的数据类型,它是唯一可以存放基本型的容器。而且Array非常地高效。 这里有一篇好文章:《历史上的 Collection 类 ― 数组》,可以帮助我们了解Array的基本情况。
Array为什么效率高呢?这要从Array本身在内存中的结构说起(下图):
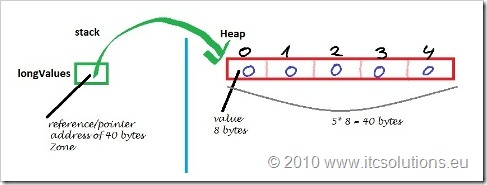 对于Array的具体实现,有下面几个重要事实:
对于Array的具体实现,有下面几个重要事实:
- Array是一个对象Object
- Array在Stack栈区只占一个“long”型,储存指向在Heap堆区的实际数据首地址的引用
- Array在Heap堆区的具体数据,所占的是“连续空间”
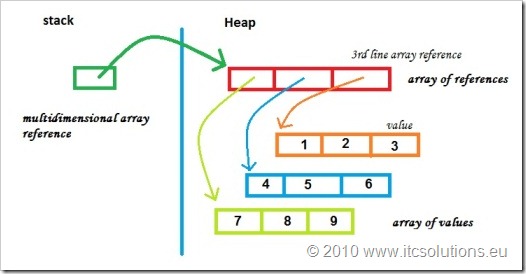 如上图,多维数组的实现方式,是靠一个“引用的数组”来过度的。第一层数组的每一个地址,只储存指向具体数据数组的一个引用。
如上图,多维数组的实现方式,是靠一个“引用的数组”来过度的。第一层数组的每一个地址,只储存指向具体数据数组的一个引用。
Array效率高的秘密,就在于它在内存中占据的空间是连续的。因此如下图,只要掌握了在内存中的首地址,以及数组的长度,对于任意想要的元素,数组只要在首地址基础上加上偏移值,就能找到该元素。而对内存的操作,seek偏移值的开销是非常小的。
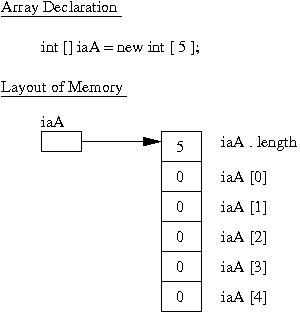
但连续空间是把双刃剑,副作用是Array声明的时候必须固定长度,之后不能修改。这极大地限制了Array的使用,因为大多数的使用场景,声明数据的时候,并不知道我们需要多大的容器。这才导致了后面其他容器的出现。
int[] myArray = new int[10];
由于Java类库已经经历了近20年的改进和打磨,java容器的效率已经有了明显的提升,尤其随着应用场景的复杂化,说Array的效率完胜容器已经不合时宜了。对一些常用的操作,比如说批量插入,或者遍历,容器提供的现成方法的效率,已经可以完胜我们自己用Array慢慢瞎捣鼓的代码了。更不用说对于更复杂的比如说并发应用。自己动手造轮子的时代已经过去了。
java.util类库中的容器
先声明,这一章只负责告诉读者一些关于util类库定义的容器的一些有用的结论,来帮助我们在编程的时候尽量选择正确合适的容器。至于容器内部的一些算法细节,会在之后的《容器深谈》这一章中探讨。
Java类库java.util提供的容器到底有哪些?下面这张图略简陋,但有助于整理思路。
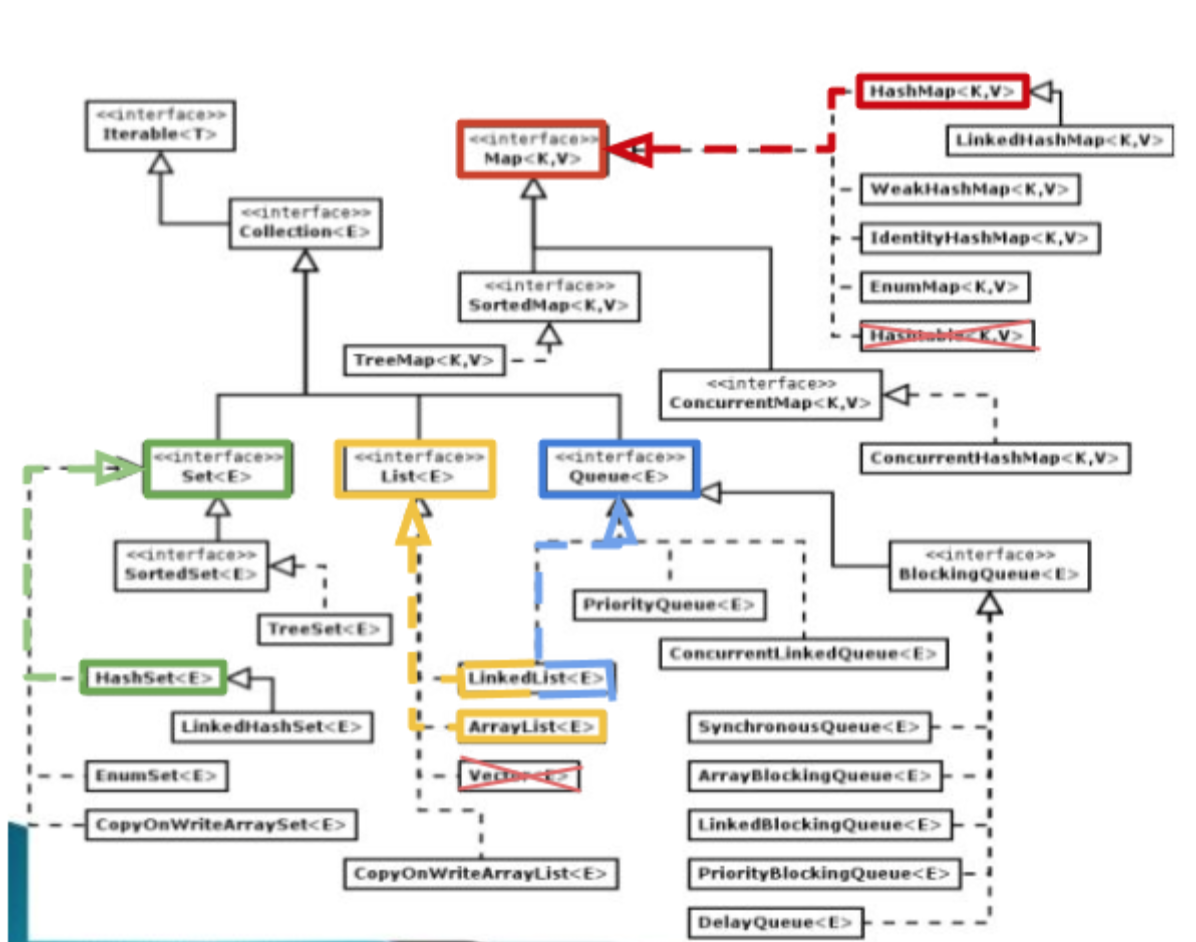
容器两大分支:Collection和Map
uitl类库容器的共同特征是:动态调节长度。为了弥补Array固定长度的遗憾。 但鱼和熊掌不可兼得。实现动态扩展数组长度,必然就要牺牲效率,为它们的弹性付出代价。因此它们的效率都不如Array。但它们之所以存在,除了动态长度外,都具备各自特色的功能,各有所长。
总的来说,容器分为两大类,都以接口形式存在,
- Collection 指的是一组元素的集合。强调的是元素本身。
- Map 的特殊功用在于它为每个元素维护的一组“KEY-VALUE”对。Key用来搜索value值。典型的应用就是“词典”。
Collection的三大将
它们也都是接口,而且各有所长,
- List:最正统。强调“一组元素的序列”。通常是元素插入集合时候的顺序。
- Set:的特点是其中元素的唯一性。插入新元素前会检查已有列表,如果已经有了,就不会再插入。
- Queue:虽然也强调的是序列,但更主要的是“获取下一个元素的顺序”。最简单的一种就是“FIFO(First In First Out)”先进先出。
关于List
事实上最常用的List只需要记住两种,
- ArrayList
- LinkedList
剩下一个Vector被作者说成是过时的容器,不推荐使用。而另一个CopyOnWriteList是用于并发系统,确保多线程访问时数据同步安全性的,不属于常规使用。
ArrayList和LinkedList它们俩个经常被拿来比较性能。互为对方一生的羁绊。关于它们俩,需要记住的重要事实是,
- ArrayList的实现基于Array。精髓在于:随机访问get(int index)方法。复杂度是常数O(1)。** 但缺点是:add(int index,
element),remove(int index)的时候要逐个前移或后移操作位后面的所有元素,所以复杂度是O(n)。 - LinkedList的精髓在于同时实现了Queue的接口。 在Queue只是个接口,以及Java官方枪毙Stack的情况下,无论是FIFO还是LIFO,都要靠LinkedList来扛起大旗。
- 总体性能ArrayList完胜。 并不像传说的LinkedList更善于插入和删除动作。LinkedList的add(int index,
element)和remove(int index)方法,复杂度要实现O(1)的前提是,你必须提前获得操作元素的引用。不然LinkedList还是需要遍历到那个元素,最坏的情况下仍然是O(n)复杂度。StackOverFlow上关于这个问题的回答:[**《How is LinkedList's add(int, E) of O(1) complexity?》**](http://stackoverflow.com/questions/15732334/how-is-linkedlists-addint-e-of-o1-complexity)
这里附上1. ArrayList和LinkedList的几个重要操作的复杂度对比:

ArrayList的实现
虽然说好了这章不细究具体实现。但还是忍不住看了一眼java.util.ArrayList的源代码。贴几个重要的片段上来,共赏。
public class ArrayList<E> extends AbstractList<E> implements List<E>, RandomAccess, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable {}
英雄先问出处,ArrayList继承自AbstractList
/**
* The array buffer into which the elements of the ArrayList are stored.
* The capacity of the ArrayList is the length of this array buffer.
*/
private transient Object[] elementData; //ArrayList基于Array实现
/**
* The size of the ArrayList (the number of elements it contains).
*
* @serial
*/
private int size;
接下来看成员字段。关键看到Object[] elementData,就知道ArrayList和传说中一样,是基于Array实现的。
/**
* Constructs an empty list with the specified initial capacity.
*/
public ArrayList(int initialCapacity) {
super();
if (initialCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+
initialCapacity);
this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity];
}
/**
* Constructs an empty list with an initial capacity of ten.
*/
public ArrayList() {
this(10); //默认长度10
}
/**
* Constructs a list containing the elements of the specified
* collection, in the order they are returned by the collection's
* iterator.
*/
public ArrayList(Collection<? extends E> c) {
elementData = c.toArray();
size = elementData.length;
// c.toArray might (incorrectly) not return Object[] (see 6260652)
if (elementData.getClass() != Object[].class)
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size, Object[].class);
}
3种构造函数,对应于3种不同的声明方式。可以看到,ArrayList的默认初始大小是10。
public boolean add(E e) {
ensureCapacity(size + 1); // Increments modCount!! 可变长度由这个方法实现
elementData[size++] = e;
return true;
}
这一段是add()方法。看到ensureCapacity(size + 1)这里,ArrayList的可变长度的功能就在这个方法里了。
/**
* Increases the capacity of this <tt>ArrayList</tt> instance, if
* necessary, to ensure that it can hold at least the number of elements
* specified by the minimum capacity argument.
*
* @param minCapacity the desired minimum capacity
*/
public void ensureCapacity(int minCapacity) {
modCount++;
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
if (minCapacity > oldCapacity) {
Object oldData[] = elementData;
int newCapacity = (oldCapacity * 3)/2 + 1; //关键算法:不够了长度就乘以1.5
if (newCapacity < minCapacity)
newCapacity = minCapacity;
// minCapacity is usually close to size, so this is a win:
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
}
}
可变长度ensureCapacity()方法长这样,代码里一行关键的算法,透露了ArrayList的动态控制长度功能,是在长度不够的时候扩展为原来的1.5倍。不要小看这个简单的1.5倍。肯定是无数次实验的最优配置。智慧的结晶啊。
不能再写下去了,这没有底。以后专门写一个读JDK源代码的笔记吧。
LinkedList的实现
java.util.LinkedList的源代码也只贴几个重要的片段上来,共赏。先看一个LinkedList数据结构的简单图解,
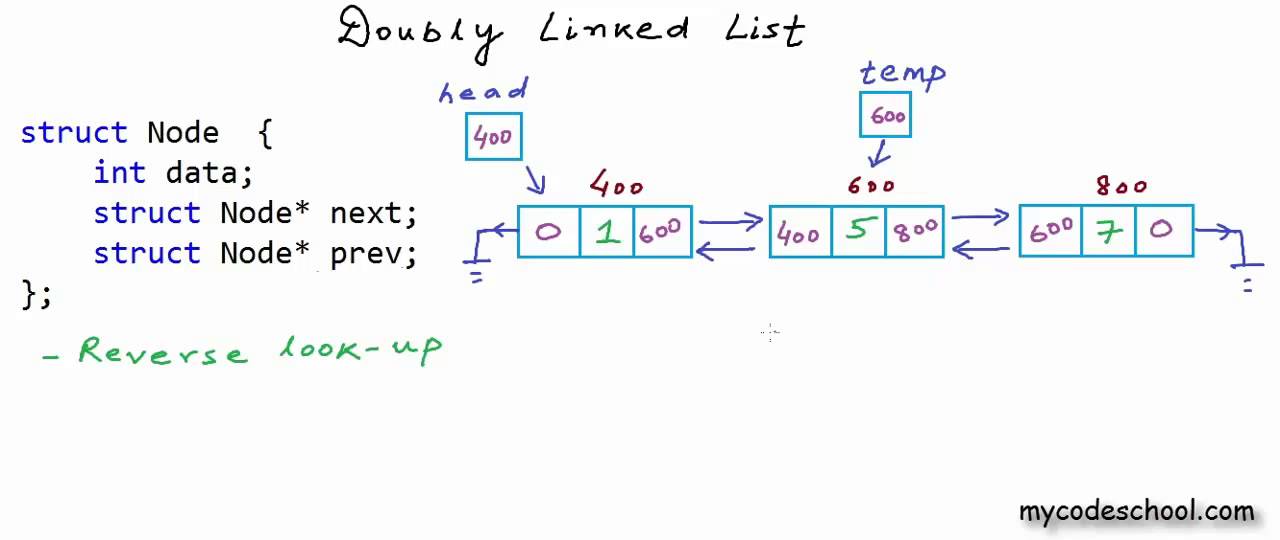 双链LinkedList的数据结构很简单,由一系列节点组成。每个节点包含一个数据储存单元,和两个指针,分别指向序列中的前一个节点,以及下一个节点。
双链LinkedList的数据结构很简单,由一系列节点组成。每个节点包含一个数据储存单元,和两个指针,分别指向序列中的前一个节点,以及下一个节点。
// 链表的表头,表头不包含任何数据。Entry是个链表类数据结构。
private transient Entry<E> header = new Entry<E>(null, null, null);
// LinkedList中元素个数
private transient int size = 0;
上面两行就能看出,LinkedList里的节点名叫Entry
// 双向链表的节点所对应的数据结构。
// 包含3部分:上一节点,下一节点,当前节点值。
private static class Entry<E> {
// 当前节点所包含的值
E element;
// 下一个节点
Entry<E> next;
// 上一个节点
Entry<E> previous;
/**
* 链表节点的构造函数。
* 参数说明:
* element —— 节点所包含的数据
* next —— 下一个节点
* previous —— 上一个节点
*/
Entry(E element, Entry<E> next, Entry<E> previous) {
this.element = element;
this.next = next;
this.previous = previous;
}
}
也很简单,就像之前说的,中间一个element泛型数据本体,一前一后两个指向前一个和下一个节点的指针。
// 将节点从链表中删除
private E remove(Entry<E> e) {
if (e == header)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
E result = e.element; //复制本体
e.previous.next = e.next; //让前一节点的指针跳过它,直接连到它的下一个节点。
e.next.previous = e.previous; //相反操作
e.next = e.previous = null; //消灭节点
e.element = null; //消灭节点
size--;
modCount++;
return result;
}
LinkedList所谓效率胜过ArrayList的remove()方法,每次删除都分两步走:
- 给目标节点的前一结点,和后一节点牵线搭桥,架空目标节点
- 删除目标节点
关于Map
已经说过,Map的特殊功用在于它为每个元素维护的一组“KEY-VALUE”对。Key用来搜索value值。选用Map的目的在于用户关心根据元素key搜寻元素value值的速度,而对元素在容器中的顺序不在乎。Map就相当于一个小型的搜索引擎。
Map手下最常用的是HashMap。它的 get(Object key) 方法效率最高。大多数情况下,能达到Array的 O(1) 的表现。我这里不想太深入,简单讲几点HashMap实现的大致原理,但实际上HashMap实现的每一步都是值得深究的。
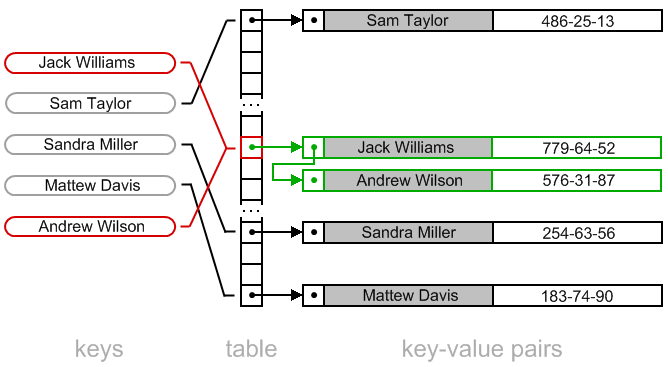 如上图,
如上图,
- HashMap是由Array和LinkedList共同组成的。(Java 8当链表太长的时候,会自动变成红黑树。)
- 先开一个很大的Array数组(size=capacity)。
- 元素直接存放在以hash值为下标的Array槽内。
- 如果碰撞了,以链表的形式存在Array槽后;
put(K key, V value) 方法的步骤如下,
- 对key的hashCode()做hash,然后再计算index;(都是简单的位操作,常数复杂度 O(1))
- 直接根据hash值来访问Array的下标。如果没碰撞直接放到bucket里;O(1);
- 如果碰撞了,以链表的形式存在buckets后;往后插的过程是要遍历链表每个节点的。所以碰撞严重的话,对HashMap的性能影响严重。
- 如果碰撞导致链表过长(大于等于TREEIFY_THRESHOLD),就把链表转换成红黑树;O(logn);
- 如果节点已经存在就替换old value(保证key的唯一性)
- 如果bucket满了(超过load factor*current capacity),就要resize。
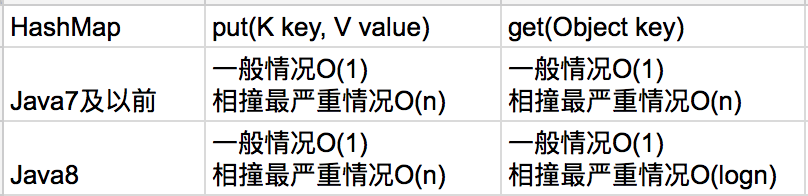
综上所述,Java 8开始改成红黑树以后,一般情况下,put(K key, V value)动作是常数复杂度O(1)。最坏情况碰撞严重,最多O(logn)。还是可以接受的。
get(Object key) 方法的步骤如下,
- bucket里的第一个节点,直接命中,O(1);
- 如果有冲突,则通过key.equals(k)去查找对应的entry
- 若为树,则在树中通过key.equals(k)查找,O(logn);
- 若为链表,则在链表中通过key.equals(k)查找,O(n)。
综上所述,和插入put()方法一样,Java 8开始改成红黑树以后,一般情况下,搜索get(Object key)动作是常数复杂度O(1)。最坏情况碰撞严重,最多O(logn)。
看下面的HashMap的源码,可以清楚地看到HashMap也是基于Array实现复杂度为O(1)的快速随机访问。
public HashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) {
if (initialCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal initial capacity: " +
initialCapacity);
if (initialCapacity > MAXIMUM_CAPACITY)
initialCapacity = MAXIMUM_CAPACITY;
if (loadFactor <= 0 || Float.isNaN(loadFactor))
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal load factor: " +
loadFactor);
// Find a power of 2 >= initialCapacity
int capacity = 1;
while (capacity < initialCapacity)
capacity <<= 1;
this.loadFactor = loadFactor;
threshold = (int)Math.min(capacity * loadFactor, MAXIMUM_CAPACITY + 1);
table = new Entry[capacity]; //这一行,证明HashMap也是基于Array实现复杂度为O(1)的快速随机访问
useAltHashing = sun.misc.VM.isBooted() &&
(capacity >= Holder.ALTERNATIVE_HASHING_THRESHOLD);
init();
}
下面这个是HashMap的hash算法。
final int hash(Object k) {
int h = 0;
if (useAltHashing) {
if (k instanceof String) {
return sun.misc.Hashing.stringHash32((String) k);
}
h = hashSeed;
}
h ^= k.hashCode(); //k的哈希值和哈希种子做异或运算(哈希种子为零,就相当于保留哈希值)
//异或:相同则结果为0,不同则结果为1
// This function ensures that hashCodes that differ only by
// constant multiples at each bit position have a bounded
// number of collisions (approximately 8 at default load factor).
h ^= (h >>> 20) ^ (h >>> 12); //h和他自己的右位移20位做异或,再和它的右位移12为做异或。
return h ^ (h >>> 7) ^ (h >>> 4); //h再和他自己的右位移7位做异或,再和它的右位移4为做异或。
}
HashMap的Hash算法具体过程如下,
- 前面一个if先不管它。
- 通过hashCode()方法获取key的哈希值,和哈希种子做异或运算(哈希种子为零,就相当于保留哈希值)(hashCode()函数先当他黑箱)
- h和他自己的右位移20位做异或,再和它的右位移12为做异或。
- h再和他自己的右位移7位做异或,再和它的右位移4为做异或。
我还不太明白这算法背后的数学意义,但一点是肯定的,从java的hash()算法因为只是简单的位操作,复杂度是常数O(1)。
我另外一个好奇的事是这个Java每个对象自带的 Object.hashCode() 方法,到底是怎么返回哈希值的。毕竟HashMap的代码也都只是在系统给的哈希值的基础上做文章。StackOverFlow该问题的最高票答案《How is hashCode() calculated in Java?》是这样说的:
hashCode()是每个对象自带的方法。但几乎每个类都会重写这个方法。所以hashCode()的哈希值计算方法每种数据类型都是不同的。
下面举两个最常用的例子,int整型的哈希值等于它本身。
public int hashCode() {
return value;
}
String的哈希值算法稍微复杂一点,基本就是根据它自身的长度迭代,每次都乘以31再加上它的偏移值。
public int hashCode() {
int h = hash;
if (h == 0) {
int off = offset;
char val[] = value;
int len = count;
//关键算法在这里
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
h = 31*h + val[off++];
}
hash = h;
}
return h;
}
对于HashMap具体的工作原理,会在以后的章节深入研究。下图总结一下HashMap的put(K key, V value)方法和get(Object key)方法的具体复杂度:
最后,如果我们希望Map中元素以某种特殊的比较顺序排列,可以用TreeMap。如果希望元素保持插入时的顺序,可以用LinkedHashMap。但效率方面就要打一点折扣了。
关于Set
前文说了Set是为了保持集合中元素的唯一性。和Map一样,同样有三种不同的实现:
- HashSet:非插入顺序,重点是get()搜索的高效。
- TreeSet:按元素的比较顺序排列。
- LinkedSet:保持插入顺序。
其中最常用的还是HashSet。TreeSet主要用于排序。排序算法取决于给定的Comparator。比如String.CASE_INSENSITIVE_ORDER.(按字母升序)
#####关于Queue Queue接口有两个主要实现:
- LinkedList:不算Queue的嫡系,但却是最常用的。经常被用来面向Queue接口编程。
- PriorityQueue:和TreeSet一样,可以根据给出的Comparator维持特定的排序。
关于Iterator迭代器和容器接口
设计Iterator迭代器的最重要原因不是为了迭代的效率。因为用普通的for语句迭代同样高效。
Iterator的真正目的是为了让使用不同容器的代码之间可以去耦合。
容器根据功能用途的不同,都被统一设计成了接口。Collection,List, Set, Map最常用的四大接口。和Iterator一样,为使用不同容器的代码去耦合才是设计这些接口的真正用意。
实际上,对于程序员自己开发的新容器而言,实现Iterator接口远比实现Collection接口要容易。因为Iterator接口只定义了hasNext()和next()两大方法。而Collection则复杂地多。因此Iterator才是简单去耦合的最佳方法。C++没有Collection接口,只有Iterator。
另外一个关于Iterator,我必须知道的是是:Java的foreach语法是面向Iterable接口的。任何类只要实现了Iterable接口都可以用foreach语法。foreach语法长这样,
for(Element e : Collection<Element>){
//do something
}
记住,所有Collection接口都实现了Iterable接口。但Maps和Array没有。
关于过时的容器
书中作者提到的明确过时的容器有三个,这三个好汉分别是:
- Vector
- HashTable
- Stack
关于Utilities
Utilities就是对于容器的一组实用静态方法。本身不需要实例化,专门用来操作对应类型的容器实例。 三大Utilities,分别用来专门操作各自的对应容器,
- Collections
- Arrays
- Maps
里面都是静态的方法。
练习
Exercise 1
- Exercise 1: (2) Create a new class called Gerbil with an int gerbilNumber that’s initialized in the constructor. Give it a method called hop( ) that displays which gerbil number this is, and that it’s hopping. Create an ArrayList and add Gerbil objects to the List. Now use the get( ) method to move through the List and call hop( ) for each Gerbil.
package com.ciaoshen.thinkinjava.chapter11;
import java.util.*;
public class Exercise1 {
public static class Gerbil {
private static int count = 0;
private final int id = ++count;
public void hop() {
System.out.println("Gerbil#" + id + " is hopping!");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Exercise1.Gerbil> list = new ArrayList<Exercise1.Gerbil>();
for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
list.add(new Exercise1.Gerbil());
}
for(Exercise1.Gerbil gerbil : list) {
gerbil.hop();
}
}
}
Exercise 2
- Exercise 2: (1) Modify SimpleCollection.java to use a Set for c.
package com.ciaoshen.thinkinjava.chapter11;
import java.util.*;
public class Exercise2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Set<Integer> c = new HashSet<Integer>();
for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
c.add(i); // Autoboxing
}
for(Integer i : c) {
System.out.print(i + ", ");
}
}
}
Exercise 3
- Exercise 3: (2) Modify innerclasses/Sequence.java so that you can add any number of elements to it.
package com.ciaoshen.thinkinjava.chapter11;
import java.util.*;
public class Exercise3 {
public static interface Selector {
boolean end();
Object current();
void next();
}
public static class Sequence {
private List<Object> items;
public Sequence() { items = new ArrayList<Object>(); }
public void add(Object x) {
items.add(x);
}
private class SequenceSelector implements Selector {
private int i = 0;
public boolean end() {
return i == items.size();
}
public Object current() {
return items.get(i);
}
public void next() {
if(i < items.size()) {
i++;
}
}
}
public Selector selector() {
return new SequenceSelector();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Sequence sequence = new Sequence();
for(int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
sequence.add(Integer.toString(i));
}
Selector selector = sequence.selector();
while(!selector.end()) {
System.out.print(selector.current() + " ");
selector.next();
}
}
}
Exercise 4
- Exercise 4:(3) Create a generator class that produces character names (as String objects) from your favorite movie (you can use Snow White or Star Wars as a fallback) each time you call next( ), and loops around to the beginning of the character list when it runs out of names. Use this generator to fill an array, an ArrayList, a LinkedList, a HashSet, a LinkedHashSet, and a TreeSet, then print each container.
Generator.java
package com.ciaoshen.thinkinjava.chapter11;
import java.util.*;
public class Exercise4 {
public static interface Generator<T> {
public T next();
}
public static class FilmGenerator implements Generator<String> {
private static final String[] FILMNAME={"肖申克的救赎", "这个杀手不太冷", "阿甘正传", "霸王别姬", "美丽人生",
"千与千寻", "辛德勒的名单", "海上钢琴师", "机器人总动员", "盗梦空间", "泰坦尼克号",
"三傻大闹宝莱坞", "放牛班的春天", "忠犬八公的故事", "大话西游", "龙猫", "教父",
"乱世佳人", "天堂电影院", "当幸福来敲门", "搏击俱乐部", "楚门的世界", "触不可及",
"指环王3","罗马假日"};
private static final int LENGTH = FILMNAME.length;
private static int count = 0;
private final int id = ++count;
private int cursor = 0;
public String next() {
if (cursor == LENGTH) {
cursor = 0;
}
return FILMNAME[cursor++];
}
}
public static Generator<String> getFilmGenerator(){
return new FilmGenerator();
}
public static String[] getFilms(String[] array) {
Generator<String> gen = getFilmGenerator();
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
array[i] = gen.next();
}
return array;
}
public static Collection<String> getFilms(Collection<String> c, int filmNum) {
Generator<String> gen = getFilmGenerator();
for (int i = 0; i < filmNum; i++) {
c.add(gen.next());
}
return c;
}
@SuppressWarnings({"unchecked","rawtypes"})
public static void main(String[] args){
int size = 10;
//fil array
System.out.println(">>>Array: ");
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(getFilms(new String[size])));
//fil arraylist
System.out.println(">>>ArrayList: ");
System.out.println(getFilms(new ArrayList(),size));
//fil lindelist
System.out.println(">>>LinkedList: ");
System.out.println(getFilms(new LinkedList(),size));
//fil hashset
System.out.println(">>>HashSet: ");
System.out.println(getFilms(new HashSet(),size));
//fil linkedhashset
System.out.println(">>>LinkedHashSet: ");
System.out.println(getFilms(new LinkedHashSet(),size));
//fil treeset
System.out.println(">>>TreeSet: ");
System.out.println(getFilms(new TreeSet(),size));
}
}
Exercise 5
- Exercise 5: (3) Modify ListFeatures.java so that it uses Integers (remember autoboxing!) instead of Pets, and explain any difference in results.
package com.ciaoshen.thinkinjava.chapter11;
import java.util.*;
public class Exercise5 {
private static final Random RAND = new Random();
private static final int MAX = 1000;
public static List<Integer> getIntegerArrayList(int size) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<Integer>();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
list.add(RAND.nextInt(MAX));
}
return list;
}
public static Integer random() {
return RAND.nextInt(MAX);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Integer> intList= getIntegerArrayList(7);
System.out.println("1: " + intList);
Integer oneInt = random();
intList.add(oneInt); // Automatically resizes
System.out.println("2: " + intList);
System.out.println("3: " + intList.contains(oneInt));
intList.remove(oneInt); // Remove by object
Integer p = intList.get(2);
System.out.println("4: " + p + " " + intList.indexOf(p));
Integer aNewInt = random();
System.out.println("5: " + intList.indexOf(aNewInt));
System.out.println("6: " + intList.remove(aNewInt));
// Must be the exact object:
System.out.println("7: " + intList.remove(p));
System.out.println("8: " + intList);
intList.add(3, random()); // Insert at an index
System.out.println("9: " + intList);
List<Integer> sub = intList.subList(1, 4);
System.out.println("subList: " + sub);
System.out.println("10: " + intList.containsAll(sub));
Collections.sort(sub); // In-place sort
System.out.println("sorted subList: " + sub);
// Order is not important in containsAll():
System.out.println("11: " + intList.containsAll(sub));
Collections.shuffle(sub, RAND); // Mix it up
System.out.println("shuffled subList: " + sub);
System.out.println("12: " + intList.containsAll(sub));
List<Integer> copy = new ArrayList<Integer>(intList);
sub = Arrays.asList(intList.get(1), intList.get(4));
System.out.println("sub: " + sub);
copy.retainAll(sub);
System.out.println("13: " + copy);
copy = new ArrayList<Integer>(intList); // Get a fresh copy
copy.remove(2); // Remove by index
System.out.println("14: " + copy);
copy.removeAll(sub); // Only removes exact objects
System.out.println("15: " + copy);
copy.set(1, random()); // Replace an element
System.out.println("16: " + copy);
copy.addAll(2, sub); // Insert a list in the middle
System.out.println("17: " + copy);
System.out.println("18: " + intList.isEmpty());
intList.clear(); // Remove all elements
System.out.println("19: " + intList);
System.out.println("20: " + intList.isEmpty());
intList.addAll(getIntegerArrayList(4));
System.out.println("21: " + intList);
Object[] o = intList.toArray();
System.out.println("22: " + o[3]);
Integer[] pa = intList.toArray(new Integer[0]);
System.out.println("23: " + pa[3]);
}
}
Exercise 6
- Exercise 6: (2) Modify ListFeatures.java so that it uses Strings instead of Pets, and explain any difference in results.
package com.ciaoshen.thinkinjava.chapter11;
import java.util.*;
public class Exercise6 {
public static interface Generator<T> {
public T next();
public List<T> createList(int listSize);
}
public static class StringGenerator implements Generator<String> {
private static final Random RAND = new Random();
private int length = 10; //number of characters in each string
public StringGenerator() {}
public StringGenerator(int len) {
length = len;
}
public List<String> createList(int listSize) {
List<String> list = new ArrayList<String>();
for (int i= 0; i < listSize; i++) {
list.add(next());
}
return list;
}
public String next() {
char[] result = new char[length];
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
char letter = (char)(((int)'a') + RAND.nextInt(26)); //random a-z
result[i] = letter;
}
return new String(result);
}
}
public static void testUnitNext(int length) {
StringGenerator gen = new StringGenerator(length);
System.out.println(gen.next());
}
public static void testUnitCreatList(int listSize) {
StringGenerator gen = new StringGenerator();
System.out.println(gen.createList(listSize));
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
/**
* Unit Test
*/
//int strLength = 7;
//testUnitNext(strLength);
//int listSize = 20;
//testUnitCreatList(listSize);
/**
* Exercise 6
*/
int strLength = 7;
int initListSize = 20;
StringGenerator gen = new StringGenerator(strLength);
List<String> list = gen.createList(initListSize);
System.out.println("1: " + list);
String str = gen.next();
list.add(str); // Automatically resizes
System.out.println("2: " + list);
System.out.println("3: " + list.contains(str));
list.remove(str); // Remove by object
String second = list.get(2);
System.out.println("4: " + second + " " + list.indexOf(second));
String str2 = gen.next();
System.out.println("5: " + list.indexOf(str2));
System.out.println("6: " + list.remove(str2));
// Must be the exact object:
System.out.println("7: " + list.remove(second));
System.out.println("8: " + list);
list.add(3, gen.next()); // Insert at an index
System.out.println("9: " + list);
List<String> sub = list.subList(1, 4);
System.out.println("subList: " + sub);
System.out.println("10: " + list.containsAll(sub));
Collections.sort(sub); // In-place sort
System.out.println("sorted subList: " + sub);
// Order is not important in containsAll():
System.out.println("11: " + list.containsAll(sub));
Collections.shuffle(sub, StringGenerator.RAND); // Mix it up
System.out.println("shuffled subList: " + sub);
System.out.println("12: " + list.containsAll(sub));
List<String> copy = new ArrayList<String>(list);
sub = Arrays.asList(list.get(1), list.get(4));
System.out.println("sub: " + sub);
copy.retainAll(sub);
System.out.println("13: " + copy);
copy = new ArrayList<String>(list); // Get a fresh copy
copy.remove(2); // Remove by index
System.out.println("14: " + copy);
copy.removeAll(sub); // Only removes exact objects
System.out.println("15: " + copy);
copy.set(1, gen.next()); // Replace an element
System.out.println("16: " + copy);
copy.addAll(2, sub); // Insert a list in the middle
System.out.println("17: " + copy);
System.out.println("18: " + list.isEmpty());
list.clear(); // Remove all elements
System.out.println("19: " + list);
System.out.println("20: " + list.isEmpty());
list.addAll(gen.createList(4));
System.out.println("21: " + list);
Object[] o = list.toArray();
System.out.println("22: " + o[3]);
String[] pa = list.toArray(new String[0]);
System.out.println("23: " + pa[3]);
}
}
Exercise 7
- Exercise 7: (3) Create a class, then make an initialized array of objects of your class. Fill a List from your array. Create a subset of your List by using subList( ), then remove this subset from your List.
package com.ciaoshen.thinkinjava.chapter11;
import java.util.*;
public class Exercise7 {
public static class Table {
private static int count = 0;
private final int ID = ++count;
public String toString() {
return "Table#" + ID;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int arrayLength = 10;
Table[] tableArray = new Table[10];
for (int i = 0; i < tableArray.length; i++) {
tableArray[i] = new Table();
}
System.out.println("Table Array >>>");
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(tableArray));
List<Table> tableList = Arrays.asList(tableArray);
System.out.println("Table list >>>");
System.out.println(tableList);
List<Table> subTableList = tableList.subList(0,tableList.size()/2);
System.out.println("Table sub list >>>");
System.out.println(subTableList);
}
}
Exercise 8
- Exercise 8: (1) Modify Exercise 1 so it uses an Iterator to move through the List while calling hop( ).
package com.ciaoshen.thinkinjava.chapter11;
import java.util.*;
public class Exercise8 {
public static class Gerbil {
private static int count = 0;
private final int ID = ++count;
public void hop() {
System.out.println("Gerbil#" + ID + " is hopping!");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Gerbil> list = new ArrayList<Gerbil>();
for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
list.add(new Gerbil());
}
Iterator<Gerbil> ite = list.iterator();
while (ite.hasNext()) {
ite.next().hop();
}
}
}
Exercise 9
- Exercise 9: (4) Modify innerclasses/Sequence.java so that Sequence works with an Iterator instead of a Selector.
package com.ciaoshen.thinkinjava.chapter11;
import java.util.*;
public class Exercise9 {
public static class Sequence implements Iterable<Object> {
private Object[] items;
private int next = 0;
public Sequence(int size) { items = new Object[size]; }
public void add(Object x) {
if (next < items.length) {
items[next++] = x;
}
}
public Iterator<Object> iterator() {
return new SequenceIterator();
}
private class SequenceIterator implements Iterator<Object> {
private int cursor = 0;
public boolean hasNext() {
return cursor < items.length;
}
public Object next() {
if (hasNext()) {
return items[cursor++];
}
return null;
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int seqLength = 10;
Sequence sequence = new Sequence(seqLength);
for(int i = 0; i < seqLength; i++) {
sequence.add(Integer.toString(i));
}
//for (Object obj : sequence) {
// System.out.println(obj);
//}
Iterator<Object> ite = sequence.iterator();
while (ite.hasNext()) {
System.out.println(ite.next());
}
}
}
Exercise 10
- Exercise 10: (2) Change Exercise 9 in the Polymorphism chapter to use an ArrayList to hold the Rodents and an Iterator to move through the sequence of Rodents.
package com.ciaoshen.thinkinjava.chapter11;
import java.util.*;
public class Exercise10 {
public static interface Rodent {
public void hop();
}
public static class Mouse implements Rodent {
private static String NAME = "Mouse";
private static int count = 0;
private int ID = ++count;
public void hop() {
System.out.println(NAME + "#" + ID + " is hopping!");
}
}
public static class Gerbil implements Rodent {
private static String NAME = "Gerbil";
private static int count = 0;
private int ID = ++count;
public void hop() {
System.out.println(NAME + "#" + ID + " is hopping!");
}
}
public static class Hamster implements Rodent {
protected static String NAME = "Hamster";
protected static int count = 0;
protected int ID = ++count;
public void hop() {
System.out.println(NAME + "#" + ID + " is hopping!");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Rodent> rodents = new ArrayList<Rodent>();
int rodentsNum = 10;
for (int i = 0; i < rodentsNum; i++) {
rodents.add(new Mouse());
rodents.add(new Gerbil());
rodents.add(new Hamster());
}
Iterator<Rodent> rodentIte = rodents.iterator();
while (rodentIte.hasNext()) {
rodentIte.next().hop();
}
}
}
Exercise 11
- Exercise 11: (2) Write a method that uses an Iterator to step through a Collection and print the toString( ) of each object in the container. Fill all the different types of Collections with objects and apply your method to each container.
package com.ciaoshen.thinkinjava.chapter11;
import java.util.*;
public class Exercise11 {
public static Collection<Object> fillCollection(Collection<Object> c, Class<?> klass, int size) {
try {
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
c.add(klass.newInstance());
}
} catch (InstantiationException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
return c;
}
public static <T> void parseCollection(Collection<T> c) {
Iterator<T> ite = c.iterator();
while (ite.hasNext()) {
System.out.println(ite.next());
}
}
public static class MyObject implements Comparable<MyObject> {
private static int count = 0;
private final int ID = ++count;
public MyObject() {}
public String toString() {
return "MyObject#" + ID + "!";
}
public int getId() {
return ID;
}
public int compareTo(MyObject o) {
return o.getId() - getId();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Class<?> klass;
try {
klass = Class.forName("com.ciaoshen.thinkinjava.chapter11.Exercise11$MyObject");
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
int size = 10;
//ArrayList
parseCollection(fillCollection(new ArrayList<Object>(), klass, size));
//LinkedList
parseCollection(fillCollection(new LinkedList<Object>(), klass, size));
//HashSet
parseCollection(fillCollection(new HashSet<Object>(), klass, size));
//TreeSet
parseCollection(fillCollection(new TreeSet<Object>(), klass, size));
//LinkedHashSet
parseCollection(fillCollection(new LinkedHashSet<Object>(), klass, size));
}
}
Exercise 12
- Exercise 12: (3) Create and populate a List
. Create a second List of the same size as the first, and use ListIterators to read elements from the first List and insert them into the second in reverse order. (You may want to explore a number of different ways to solve this problem.)
package com.ciaoshen.thinkinjava.chapter11;
import java.util.*;
public class Exercise12 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Random rand = new Random();
List<Integer> list1 = new ArrayList<Integer>();
List<Integer> list2 = new ArrayList<Integer>();
int listSize = 10;
int max = 1000;
for (int i = 0; i < listSize; i++) {
list1.add(new Integer(rand.nextInt(max)));
list2.add(new Integer(rand.nextInt(max)));
}
ListIterator<Integer> ite = list1.listIterator(list1.size());
while (ite.hasPrevious()) {
list2.add(ite.previous());
}
System.out.println(list1);
System.out.println(list2);
}
}
Exercise 13
- Exercise 13: (3) In the innerclasses/GreenhouseController.java example, the class Controller uses an ArrayList. Change the code to use a LinkedList instead, and use an Iterator to cycle through the set of events.
package com.ciaoshen.thinkinjava.chapter11;
import java.util.*;
public class Exercise13 {
public static class Controller {
private List<Event> eventList = new ArrayList<Event>();
public void addEvent(Event c) { eventList.add(c); }
public void run() {
while(eventList.size() > 0) {
// Make a copy so you’re not modifying the list
// while you’re selecting the elements in it:
for(Event e : new ArrayList<Event>(eventList)) {
if(e.ready()) {
System.out.println(e);
e.action();
eventList.remove(e);
}
}
}
}
}
public static abstract class Event {
private long eventTime;
protected final long delayTime;
public Event(long delayTime) {
this.delayTime = delayTime;
start();
}
public void start() { // Allows restarting
eventTime = System.nanoTime() + delayTime;
}
public boolean ready() {
return System.nanoTime() >= eventTime;
}
public abstract void action();
}
public static class GreenhouseControls extends Controller {
private boolean light = false;
public class LightOn extends Event {
public LightOn(long delayTime) { super(delayTime); }
public void action() {
// Put hardware control code here to
// physically turn on the light.
light = true;
}
public String toString() { return "Light is on"; }
}
public class LightOff extends Event {
public LightOff(long delayTime) { super(delayTime); }
public void action() {
// Put hardware control code here to
// physically turn off the light.
light = false;
}
public String toString() { return "Light is off"; }
}
private boolean water = false;
public class WaterOn extends Event {
public WaterOn(long delayTime) { super(delayTime); }
public void action() {
// Put hardware control code here.
water = true;
}
public String toString() {
return "Greenhouse water is on";
}
}
public class WaterOff extends Event {
public WaterOff(long delayTime) { super(delayTime); }
public void action() {
// Put hardware control code here.
water = false;
}
public String toString() {
return "Greenhouse water is off";
}
}
private String thermostat = "Day";
public class ThermostatNight extends Event {
public ThermostatNight(long delayTime) {
super(delayTime);
}
public void action() {
// Put hardware control code here.
thermostat = "Night";
}
public String toString() {
return "Thermostat on night setting";
}
}
public class ThermostatDay extends Event {
public ThermostatDay(long delayTime) {
super(delayTime);
}
public void action() {
// Put hardware control code here.
thermostat = "Day";
}
public String toString() {
return "Thermostat on day setting";
}
}
// An example of an action() that inserts a
// new one of itself into the event list:
public class Bell extends Event {
public Bell(long delayTime) { super(delayTime); }
public void action() {
addEvent(new Bell(delayTime));
}
public String toString() { return "Bing!"; }
}
public class Restart extends Event {
private List<Event> eventList;
public Restart(long delayTime, List<Event> eventList) {
super(delayTime);
this.eventList = eventList;
for(Event e : eventList)
addEvent(e);
}
public void action() {
for(Event e : eventList) {
e.start(); // Rerun each event
addEvent(e);
}
start(); // Rerun this Event
addEvent(this);
}
public String toString() {
return "Restarting system";
}
}
public static class Terminate extends Event {
public Terminate(long delayTime) { super(delayTime); }
public void action() { System.exit(0); }
public String toString() { return "Terminating"; }
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
GreenhouseControls gc = new GreenhouseControls();
// Instead of hard-wiring, you could parse
// configuration information from a text file here:
gc.addEvent(gc.new Bell(900));
List<Event> eventList = new LinkedList<Event>();
eventList.add(gc.new ThermostatNight(0));
eventList.add(gc.new LightOn(200));
eventList.add(gc.new LightOff(400));
eventList.add(gc.new WaterOn(600));
eventList.add(gc.new WaterOff(800));
eventList.add(gc.new ThermostatDay(1400));
gc.addEvent(gc.new Restart(2000, eventList));
int delayTime = 5000;
gc.addEvent(new GreenhouseControls.Terminate(new Integer(delayTime)));
gc.run();
}
}
Exercise 14
- Exercise 14: (3) Create an empty LinkedList
. Using a ListIterator, add Integers to the List by always inserting them in the middle of the List.
package com.ciaoshen.thinkinjava.chapter11;
import java.util.*;
public class Exercise14 {
public static List<Integer> insertInMiddle(List<Integer> list, Integer num) { //insert a num 1-1000 in the middle of the list
int halfLength = list.size()/2;
ListIterator<Integer> ite = list.listIterator();
List<Integer> resultList = new LinkedList<Integer>();
for (int i = 0; i < halfLength; i++) {
resultList.add(ite.next());
}
resultList.add(num);
while (ite.hasNext()) {
resultList.add(ite.next());
}
return resultList;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Integer> list = new LinkedList<Integer>();
int times = 10;
for (int i = 0; i < times; i++) {
list = insertInMiddle(list,i);
}
System.out.println(list);
}
}
Exercise 15
- Exercise 15: (4) Stacks are often used to evaluate expressions in programming languages. Using net.mindview.util.Stack, evaluate the following expression, where’+’ means “push the following letter onto the stack,” and’-’ means “pop the top of the stack and print it”: “+U+n+c—+e+r+t—+a-+i-+n+t+y—+ -+r+u—+l+e+s—”
这题我用LinkedList自己实现了一个Stack。
package com.ciaoshen.thinkinjava.chapter11;
import java.util.*;
public class Exercise15 {
private LinkedList<String> list = new LinkedList<String>();
public boolean empty() {
return list.size() == 0;
}
public String peek() {
return list.peek();
}
public String pop() {
return list.pop();
}
public String push(String item) {
list.addFirst(item);
return item;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public int search(Object o) {
return list.indexOf((String)o);
}
public String toString() {
return list.toString();
}
public static interface Generator<T> {
public T next();
}
public class StringGenerator implements Generator<String> {
private int length = 7;
private final Random RAND = new Random();
public StringGenerator(int l) {
length = l;
}
public String next() {
char[] charArray = new char[length];
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
char c = (char)((int)'a' + RAND.nextInt(26));
charArray[i] = c;
}
return new String(charArray);
}
}
public Generator<String> generator(int length) {
return this.new StringGenerator(length);
}
enum ScanStatus {READ, WRITE}
public class CommentErrorException extends Exception {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 0;
public CommentErrorException(String offset) { //offset is the index where the error occurs
super(offset);
}
}
public void scanComment(String comment) throws CommentErrorException {
ScanStatus myStatus = ScanStatus.WRITE;
List<String> commentList = Arrays.asList(comment.split(""));
ListIterator<String> commentIte = commentList.listIterator();
String cursor = ""; //current comment
int offset = 0; //index of cursor
while (commentIte.hasNext()) {
offset = commentIte.nextIndex();
cursor = commentIte.next();
if (myStatus == ScanStatus.WRITE) {
if (cursor.equals("+")) {
myStatus = ScanStatus.READ;
continue;
}
if (cursor.equals("-")) {
if (empty()) {
throw new CommentErrorException("Position " + Integer.toString(offset) + ": stack is empty! nothing to pop!");
}
System.out.print(pop());
continue;
}
throw new CommentErrorException("Got \"" + cursor + "\" at position " + Integer.toString(offset) + ": need +- operation here!");
}
if (myStatus == ScanStatus.READ) {
list.push(cursor);
myStatus = ScanStatus.WRITE;
continue;
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Exercise15 stack = new Exercise15();
int stackLength = 10;
for (int i = 0; i < stackLength; i++) {
stack.push(Integer.toString(i));
}
System.out.println(stack);
while (!stack.empty()) {
System.out.println(stack.pop());
}
System.out.println("Stack is empty? " + stack.empty());
String comment = "+U+n+c-+e+r+t-+a-+i-+n+t+y-+ -+r+u-+l+e+s-";
try {
stack.scanComment(comment);
} catch(CommentErrorException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
Exercise 16
- Exercise 16: (5) Create a Set of the vowels. Working from UniqueWords.Java, count and display the number of vowels in each input word, and also display the total number of vowels in the input file.
package com.ciaoshen.thinkinjava.chapter11;
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.regex.*;
public class Exercise16 {
private static final String SPLITER = "\n";
//read file
public static String readFile(String path) {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
try {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(new File(path)));
try {
String line = new String("");
while (true) {
line = br.readLine();
if (line == null) {break;}
sb.append(line + SPLITER);
}
} finally {
br.close();
}
} catch(FileNotFoundException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} catch(IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
return sb.toString();
}
//word segment
public static Map<String,Integer> segmentWords(String content) {
if (content == null || content.isEmpty()) {
throw new RuntimeException("Content for segmentWords() method is null or empty!");
}
Map<String,Integer> freqMap = new HashMap<String,Integer>();
Pattern wordP = Pattern.compile("\\w+");
Matcher wordM = wordP.matcher(content);
String word = "";
while (wordM.find()) {
word = wordM.group();
if (freqMap.containsKey(word)) {
freqMap.put(word, freqMap.get(word)+1);
continue;
}
freqMap.put(word, 1);
}
return freqMap;
}
//count vowels
public static void countVowels(Map<String, Integer> wordsMap) {
int totalVowelNum = 0;
int wordVowelCount = 0;
Pattern vowelP = Pattern.compile("[aeiouAEIOU]");
Matcher vowelM = vowelP.matcher("");
if (wordsMap == null || wordsMap.isEmpty()) {
throw new RuntimeException("The wordsMap for countVowels() method is null or empty!");
}
Formatter f = new Formatter(System.out);
f.format("%-20.20s | %5s %5.5s \n", "WORD", "VOWEL", "FQ");
f.format("%-35.35s \n", "----------------------------------------------");
for (Map.Entry<String,Integer> record : wordsMap.entrySet()) {
wordVowelCount = 0;
vowelM = vowelM.reset(record.getKey());
while (vowelM.find()) {
wordVowelCount++;
}
f.format("%-20.20s | %5d %5.5s \n", record.getKey(), wordVowelCount, "*" + Integer.toString(record.getValue()));
totalVowelNum += wordVowelCount * record.getValue();
}
f.format("%-35.35s \n", "---------------------------------------------");
f.format("%-20.20s | %5.5s \n", "Total Vowel:", Integer.toString(totalVowelNum));
}
//test Unit
private static class UnitTest {
private static final String WRONGPATH = "/Users/HelloKitty/hello.java";
private static final String RIGHTPATH = "/Users/Wei/java/com/ciaoshen/thinkinjava/chapter11/Exercise16.java";
private static void testReadFile() {
System.out.println(readFile(WRONGPATH));
System.out.println(readFile(RIGHTPATH));
}
private static void testSegmentWords() {
System.out.println(segmentWords(readFile(RIGHTPATH)));
}
private static void testCountVowels() {
countVowels(segmentWords(readFile(RIGHTPATH)));
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
//UnitTest.testReadFile();
//UnitTest.testSegmentWords();
UnitTest.testCountVowels();
}
}
Exercise 17
- Exercise 17: (2) Take the Gerbil class in Exercise 1 and put it into a Map instead, associating each Gerbil’s name (e.g. “Fuzzy” or “Spot”) as a String (the key) for each Gerbil (the value) you put in the table. Get an Iterator for the keySet( ) and use it to move through the Map, looking up the Gerbil for each key and printing out the key and telling the Gerbil to hop( ).
package com.ciaoshen.thinkinjava.chapter11;
import java.util.*;
public class Exercise17 {
public static class Gerbil {
private static int count = 0;
private final int id = ++count;
private final String name;
public Gerbil(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void hop() {
System.out.println("Gerbil#" + id + ": " + name + ", is hopping!");
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Gerbil fuzzy = new Gerbil("Fuzzy");
Gerbil spot = new Gerbil("Spot");
Gerbil piupiu = new Gerbil("PiuPiu");
Map<String, Gerbil> gerbilMap = new HashMap<String, Gerbil>();
gerbilMap.put(fuzzy.getName(),fuzzy);
gerbilMap.put(spot.getName(),spot);
gerbilMap.put(piupiu.getName(),piupiu);
Iterator<Map.Entry<String, Gerbil>> ite = gerbilMap.entrySet().iterator();
while (ite.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry<String, Gerbil> entry = ite.next();
System.out.print("(Gerbil: " + entry.getKey() + ") >>> ");
entry.getValue().hop();
}
}
}
Exercise 18
Exercise 18: (3) Fill a HashMap with key-value pairs. Print the results to show ordering by hash code. Extract the pairs, sort by key, and place the result into a LinkedHashMap. Show that the insertion order is maintained.
package com.ciaoshen.thinkinjava.chapter11;
import java.util.*;
public class Exercise18 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// insert HashMap
Map<String, Integer> hashMap = new HashMap<String, Integer>();
hashMap.put("one", 1);
hashMap.put("two", 2);
hashMap.put("three", 3);
hashMap.put("four", 4);
hashMap.put("five", 5);
// print HashMap
System.out.println(hashMap);
// extract to ArrayList
Set<Map.Entry<String,Integer>> set = hashMap.entrySet();
List<Map.Entry<String,Integer>> list = new ArrayList<Map.Entry<String,Integer>>();
list.addAll(set);
// sort ArrayList
Collections.sort(list, new Comparator<Map.Entry<String,Integer>>() {
public int compare(Map.Entry<String,Integer> entry1, Map.Entry<String,Integer> entry2) {
return Integer.compare(entry1.getValue(), entry2.getValue());
}
});
// insert into LinkedHashMap
Map<String,Integer> linkedHashMap = new LinkedHashMap<String,Integer>();
for (Map.Entry<String,Integer> entry : list) {
linkedHashMap.put(entry.getKey(), entry.getValue());
}
// print LinkedHashMap
System.out.println(linkedHashMap);
}
}
Exercise 19
- Exercise 19: (2) Repeat the previous exercise with a HashSet and LinkedHashSet.
package com.ciaoshen.thinkinjava.chapter11;
import java.util.*;
public class Exercise19 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// fill HashSet
HashSet<String> hashSet = new HashSet<String>();
hashSet.add("one");
hashSet.add("two");
hashSet.add("three");
hashSet.add("four");
hashSet.add("five");
// print HashSet
System.out.println(hashSet);
// transit to list
List<String> list = new ArrayList<String>();
list.addAll(hashSet);
// sort list
Collections.sort(list, String.CASE_INSENSITIVE_ORDER);
// insert into LinkedHashSet
Set<String> linkedHashSet = new LinkedHashSet<String>();
linkedHashSet.addAll(list);
// print LinkedHashSet
System.out.println(linkedHashSet);
}
}
Exercise 20
- Exercise 20: (3) Modify Exercise 16 so that you keep a count of the occurrence of each vowel.
package com.ciaoshen.thinkinjava.chapter11;
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.regex.*;
public class Exercise20 {
private static final String SPLITER = "\n";
//read file
public static String readFile(String path) {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
try {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(new File(path)));
try {
String line = new String("");
while (true) {
line = br.readLine();
if (line == null) {break;}
sb.append(line + SPLITER);
}
} finally {
br.close();
}
} catch(FileNotFoundException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} catch(IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
return sb.toString();
}
//word segment
public static Map<String,Integer> segmentWords(String content) {
if (content == null || content.isEmpty()) {
throw new RuntimeException("Content for segmentWords() method is null or empty!");
}
Map<String,Integer> freqMap = new HashMap<String,Integer>();
Pattern wordP = Pattern.compile("\\w+");
Matcher wordM = wordP.matcher(content);
String word = "";
while (wordM.find()) {
word = wordM.group();
if (freqMap.containsKey(word)) {
freqMap.put(word, freqMap.get(word)+1);
continue;
}
freqMap.put(word, 1);
}
return freqMap;
}
//count vowels
public static void countVowels(Map<String, Integer> wordsMap) {
int totalVowelNum = 0;
int wordVowelCount = 0;
int aCount = 0;
int eCount = 0;
int iCount = 0;
int oCount = 0;
int uCount = 0;
Pattern vowelP = Pattern.compile("[aeiouAEIOU]");
Matcher vowelM = vowelP.matcher("");
Matcher aM = Pattern.compile("[aA]").matcher("");
Matcher eM = Pattern.compile("[eE]").matcher("");
Matcher iM = Pattern.compile("[iI]").matcher("");
Matcher oM = Pattern.compile("[oO]").matcher("");
Matcher uM = Pattern.compile("[uU]").matcher("");
if (wordsMap == null || wordsMap.isEmpty()) {
throw new RuntimeException("The wordsMap for countVowels() method is null or empty!");
}
Formatter f = new Formatter(System.out);
f.format("%-20.20s | %5s %5.5s \n", "WORD", "VOWEL", "FQ");
f.format("%-35.35s \n", "----------------------------------------------");
for (Map.Entry<String,Integer> record : wordsMap.entrySet()) {
wordVowelCount = 0;
String word = record.getKey();
vowelM = vowelM.reset(word);
while (vowelM.find()) {
wordVowelCount++;
}
aM = aM.reset(word);
while (aM.find()) {
aCount++;
}
eM = eM.reset(word);
while (eM.find()) {
eCount++;
}
iM = iM.reset(word);
while (iM.find()) {
iCount++;
}
oM = oM.reset(word);
while (oM.find()) {
oCount++;
}
uM = uM.reset(word);
while (uM.find()) {
uCount++;
}
f.format("%-20.20s | %5d %5.5s \n", record.getKey(), wordVowelCount, "*" + Integer.toString(record.getValue()));
totalVowelNum += wordVowelCount * record.getValue();
}
f.format("%-35.35s \n", "---------------------------------------------");
f.format("%-20.20s | %5.5s \n", "Total a/A:", Integer.toString(aCount));
f.format("%-20.20s | %5.5s \n", "Total e/E:", Integer.toString(eCount));
f.format("%-20.20s | %5.5s \n", "Total i/I:", Integer.toString(iCount));
f.format("%-20.20s | %5.5s \n", "Total o/O:", Integer.toString(oCount));
f.format("%-20.20s | %5.5s \n", "Total u/U:", Integer.toString(uCount));
f.format("%-20.20s | %5.5s \n", "Total Vowel:", Integer.toString(totalVowelNum));
}
//test Unit
private static class UnitTest {
private static final String WRONGPATH = "/Users/HelloKitty/hello.java";
private static final String RIGHTPATH = "/Users/Wei/java/com/ciaoshen/thinkinjava/chapter11/Exercise16.java";
private static void testReadFile() {
System.out.println(readFile(WRONGPATH));
System.out.println(readFile(RIGHTPATH));
}
private static void testSegmentWords() {
System.out.println(segmentWords(readFile(RIGHTPATH)));
}
private static void testCountVowels() {
countVowels(segmentWords(readFile(RIGHTPATH)));
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
//UnitTest.testReadFile();
//UnitTest.testSegmentWords();
UnitTest.testCountVowels();
}
}
Exercise 21
- Exercise 21: (3) Using a Map<String,Integer>, follow the form of UniqueWords.java to create a program that counts the occurrence of words in a file. Sort the results using Collections.sort( ) with a second argument of String.CASE_INSENSITIVE_ORDER (to produce an alphabetic sort), and display the result.
MyReader.java
package com.ciaoshen.thinkinjava.chapter11;
import java.io.*;
public class MyReader {
private static String spliter = "\n";
public MyReader(){}
public MyReader(String s) {
spliter = s;
}
public String readFile(String path) {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
try {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(new File(path)));
String line = "";
try {
while (true) {
line = br.readLine();
if (line == null) {
break;
}
sb.append(line + spliter);
}
} finally {
br.close();
}
} catch(FileNotFoundException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} catch(IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
return sb.toString();
}
private class TestUnit {
private final String WRONGPATH = "/Users/HelloKitty/hello.java";
private final String RIGHTPATH = "/Users/Wei/java/com/ciaoshen/thinkinjava/chapter11/MyReader.java";
private void testReadFile() {
System.out.println(readFile(RIGHTPATH));
System.out.println(readFile(WRONGPATH));
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
TestUnit test = new MyReader().new TestUnit();
test.testReadFile();
}
}
Exercise21.java
package com.ciaoshen.thinkinjava.chapter11;
import java.util.*;
import java.util.regex.*;
public class Exercise21 {
private static Map<String, Integer> uniqueWords(String path) {
MyReader reader = new MyReader();
String content = reader.readFile(path);
if (content == null || content.isEmpty()) {
throw new RuntimeException(path + " is null or empty!");
}
Matcher wordM = Pattern.compile("\\w+").matcher(content);
Map<String,Integer> wordsMap = new HashMap<String,Integer>();
String word = "";
while (wordM.find()) {
word = wordM.group();
if (wordsMap.containsKey(word)) {
wordsMap.put(word,wordsMap.get(word) + 1);
continue;
}
wordsMap.put(word,1);
}
return wordsMap;
}
public static Map<String, Integer> sortedUniqueWords(String path) {
Map<String,Integer> wordsMap = uniqueWords(path);
if (wordsMap == null || wordsMap.isEmpty()) {
throw new RuntimeException("The words map for the file " + path + " is null or empty!");
}
List<String> list = new ArrayList<String>();
list.addAll(wordsMap.keySet());
Collections.sort(list, String.CASE_INSENSITIVE_ORDER);
Map<String, Integer> linkedHashMap = new LinkedHashMap<String, Integer>();
for (String word : list) {
Integer feq = wordsMap.get(word);
if (feq == null) {
continue;
}
linkedHashMap.put(word, feq);
}
return linkedHashMap;
}
public static void display(Map<String, Integer> map) {
if (map == null || map.isEmpty()) {
throw new RuntimeException("The args Map for display() method is null or empty!");
}
Formatter f = new Formatter(System.out);
f.format("%1$20.20s %2$-5.5s \n", "WORD", "FQ");
Set<Map.Entry<String, Integer>> set = map.entrySet();
for (Map.Entry<String, Integer> entry : set) {
f.format("%1$20.20s %2$-5d \n", entry.getKey(), entry.getValue());
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String path = "/Users/Wei/java/com/ciaoshen/thinkinjava/chapter11/Exercise21.java";
//System.out.println(uniqueWords(path));
//System.out.println(sortedUniqueWords(path));
display(sortedUniqueWords(path));
}
}
Exercise 22
- Exercise 22: (5) Modify the previous exercise so that it uses a class containing a String and a count field to store each different word, and a Set of these objects to maintain the list of words.
MyReader.java
package com.ciaoshen.thinkinjava.chapter11;
import java.io.*;
public class MyReader {
private static String spliter = "\n";
public MyReader(){}
public MyReader(String s) {
spliter = s;
}
public String readFile(String path) {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
try {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(new File(path)));
String line = "";
try {
while (true) {
line = br.readLine();
if (line == null) {
break;
}
sb.append(line + spliter);
}
} finally {
br.close();
}
} catch(FileNotFoundException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} catch(IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
return sb.toString();
}
private class TestUnit {
private final String WRONGPATH = "/Users/HelloKitty/hello.java";
private final String RIGHTPATH = "/Users/Wei/java/com/ciaoshen/thinkinjava/chapter11/MyReader.java";
private void testReadFile() {
System.out.println(readFile(RIGHTPATH));
System.out.println(readFile(WRONGPATH));
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
TestUnit test = new MyReader().new TestUnit();
test.testReadFile();
}
}
Exercise22.java
package com.ciaoshen.thinkinjava.chapter11;
import java.util.*;
import java.util.regex.*;
public class Exercise22 {
private static class Pair implements Comparable<Pair> {
private String key = "";
private int value = 0;
public Pair() {}
public Pair(String word, int freq) {
key = word;
value = freq;
}
public String getKey() {
return key;
}
public int getValue() {
return value;
}
public void setKey(String word) {
key = word;
}
public void setValue(int freq) {
value = freq;
}
public String toString() {
return "(" + key + "," + value + ")";
}
public int compareTo(Pair p) {
return String.CASE_INSENSITIVE_ORDER.compare(this.key, p.getKey());
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
Pair p = (Pair)o;
return this.key.equals(p.getKey());
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return this.key.hashCode();
}
}
private static Set<Pair> uniqueWords(String path) {
MyReader reader = new MyReader();
String content = reader.readFile(path);
if (content == null || content.isEmpty()) {
throw new RuntimeException(path + " is null or empty!");
}
Matcher wordM = Pattern.compile("\\w+").matcher(content);
Set<Pair> pairSet = new HashSet<Pair>();
while (wordM.find()) {
Pair word = new Pair(wordM.group(), 1);
if (pairSet.contains(word)) {
if (updateSet(pairSet, word)) {
continue;
}
}
pairSet.add(word);
}
return pairSet;
}
private static boolean updateSet(Set<Pair> set, Pair p) {
Iterator<Pair> ite = set.iterator();
while (ite.hasNext()) {
Pair current = ite.next();
if (current.equals(p)) {
String key = current.getKey();
int freq = current.getValue();
Pair newPair = new Pair(key, freq + 1);
set.remove(p);
set.add(newPair);
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
public static List<Pair> sortedUniqueWords(String path) {
Set<Pair> pairSet = uniqueWords(path);
if (pairSet == null || pairSet.isEmpty()) {
throw new RuntimeException("The pair set for the file " + path + " is null or empty!");
}
List<Pair> list = new ArrayList<Pair>();
list.addAll(pairSet);
Collections.sort(list);
return list;
}
public static void display(List<Pair> list) {
if (list == null || list.isEmpty()) {
throw new RuntimeException("The args list for display() method is null or empty!");
}
Formatter f = new Formatter(System.out);
f.format("%1$20.20s %2$-5.5s \n", "WORD", "FQ");
for (Pair pair : list) {
f.format("%1$20.20s %2$-5d \n", pair.getKey(), pair.getValue());
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String path = "/Users/Wei/java/com/ciaoshen/thinkinjava/chapter11/Exercise21.java";
//System.out.println(uniqueWords(path));
//System.out.println(sortedUniqueWords(path));
display(sortedUniqueWords(path));
}
}
Exercise 23
- Exercise 23: (4) Starting with Statistics.java, create a program that runs the test repeatedly and looks to see if any one number tends to appear more than the others in the results.
package com.ciaoshen.thinkinjava.chapter11;
import java.util.*;
public class Exercise23 {
private static Map<Integer,Integer> randomNum(int size) {
Random rand = new Random();
Map<Integer,Integer> m = new HashMap<Integer,Integer>();
for(int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
// Produce a number between 0 and 20:
int r = rand.nextInt(size);
Integer freq = m.get(r);
m.put(r, freq == null ? 1 : freq + 1);
}
return m;
}
// merge the second map to the first map
private static Map<Integer,Integer> mergeMap(Map<Integer,Integer> map1, Map<Integer,Integer> map2) {
if (map1 == null || map1.isEmpty() || map2 == null || map2.isEmpty()) {
return map1;
}
Set<Map.Entry<Integer,Integer>> set1 = map1.entrySet();
Set<Map.Entry<Integer,Integer>> set2 = map2.entrySet();
Map<Integer,Integer> result = new HashMap<Integer,Integer>();
for (Map.Entry<Integer,Integer> entry1 : set1) {
Integer key1 = entry1.getKey();
Integer value1 = entry1.getValue();
for (Map.Entry<Integer,Integer> entry2 : set2) {
Integer key2 = entry2.getKey();
Integer value2 = entry2.getValue();
if (key2 != null && value2 != null && key2.equals(key1)) {
result.put(key1, value1 + entry2.getValue());
break;
}
result.put(key1,value1);
}
}
return result;
}
public static Map<Integer,Integer> repeatRandomNum(int times, int size) {
Map<Integer,Integer> result = randomNum(size);
for (int i = 0; i < times-1; i++) {
result = mergeMap(result,randomNum(size));
}
return result;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(repeatRandomNum(10,20));
}
}
Exercise 24
- Exercise 24: (2) Fill a LinkedHashMap with String keys and objects of your choice. Now extract the pairs, sort them based on the keys, and reinsert them into the Map.
package com.ciaoshen.thinkinjava.chapter11;
import java.util.*;
public class Exercise24 {
public static class Dog {
private static int count = 0;
private final int ID = ++count;
private final String NAME;
public Dog(String name) {
NAME = name;
}
public String toString() {
return "Dog#" + ID + " called " + NAME;
}
}
public static String randomName(int length) {
Random rand = new Random();
char[] name = new char[length];
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
name[i] = (char)((int)'a' + rand.nextInt(26));
}
return new String(name);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String,Dog> dogMap = new LinkedHashMap<String,Dog>();
int mapSize = 20;
int nameLength =4;
for (int i = 0; i < mapSize; i++) {
String dogName = randomName(nameLength);
dogMap.put(dogName,new Dog(dogName));
}
//System.out.println(dogMap);
Set<Map.Entry<String,Dog>> dogSet = dogMap.entrySet();
List<Map.Entry<String,Dog>> dogList = new ArrayList<Map.Entry<String,Dog>>();
dogList.addAll(dogSet);
//System.out.println(dogList);
Collections.sort(dogList, new Comparator<Map.Entry<String,Dog>>() {
public int compare(Map.Entry<String,Dog> entry1, Map.Entry<String,Dog> entry2) {
return String.CASE_INSENSITIVE_ORDER.compare(entry1.getKey(),entry2.getKey());
}
});
//System.out.println(dogList);
Map<String,Dog> sortedDogMap = new LinkedHashMap<String,Dog>();
for (Map.Entry<String,Dog> entry : dogList) {
sortedDogMap.put(entry.getKey(),entry.getValue());
}
System.out.println(sortedDogMap);
}
}
Exercise 25
- Exercise 25: (3) Create a Map<String,ArrayList
>. Use net.mindview.TextFile to open a text file and read it in a word at a time (use "\\W+" as the second argument to the TextFile constructor). Count the words as you read them in, and for each word in the file, record in the ArrayList the word count associated with that word—this is, in effect, the location in the file where that word was found.
MyReader.java
package com.ciaoshen.thinkinjava.chapter11;
import java.io.*;
public class MyReader {
private static String spliter = "\n";
public MyReader(){}
public MyReader(String s) {
spliter = s;
}
public String readFile(String path) {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
try {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(new File(path)));
String line = "";
try {
while (true) {
line = br.readLine();
if (line == null) {
break;
}
sb.append(line + spliter);
}
} finally {
br.close();
}
} catch(FileNotFoundException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} catch(IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
return sb.toString();
}
private class TestUnit {
private final String WRONGPATH = "/Users/HelloKitty/hello.java";
private final String RIGHTPATH = "/Users/Wei/java/com/ciaoshen/thinkinjava/chapter11/MyReader.java";
private void testReadFile() {
System.out.println(readFile(RIGHTPATH));
System.out.println(readFile(WRONGPATH));
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
TestUnit test = new MyReader().new TestUnit();
test.testReadFile();
}
}
Exercise25.java
package com.ciaoshen.thinkinjava.chapter11;
import java.util.*;
import java.util.regex.*;
// statistics the word and their positions in the file
public class Exercise25 {
public static Map<String,ArrayList<Integer>> statistic(String path, String regex) {
if (path == null || regex == null) {
throw new RuntimeException("Argument content or regex is null!");
}
String content = new MyReader().readFile(path);
if (content == null) {
throw new RuntimeException("The content in " + path + " is null!");
}
Matcher matcher = Pattern.compile(regex).matcher(content);
Map<String,ArrayList<Integer>> result = new HashMap<String,ArrayList<Integer>>();
ArrayList<Integer> value = new ArrayList<Integer>();
String key = "";
while (matcher.find()) {
key = matcher.group();
if (result.containsKey(key)) {
value = result.get(key);
value.add(matcher.start());
result.put(key,value);
continue;
}
result.put(matcher.group(), new ArrayList<Integer>(Arrays.asList(matcher.start())));
}
return result;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String path = "/Users/Wei/java/com/ciaoshen/thinkinjava/chapter11/Exercise25.java";
String regex = "\\w+";
System.out.println(statistic(path,regex));
}
}
Exercise 26
- Exercise 26: (4) Take the resulting Map from the previous exercise and re-create the order of the words as they appeared in the original file.
MyReader.java
package com.ciaoshen.thinkinjava.chapter11;
import java.io.*;
public class MyReader {
private static String spliter = "\n";
public MyReader(){}
public MyReader(String s) {
spliter = s;
}
public String readFile(String path) {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
try {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(new File(path)));
String line = "";
try {
while (true) {
line = br.readLine();
if (line == null) {
break;
}
sb.append(line + spliter);
}
} finally {
br.close();
}
} catch(FileNotFoundException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} catch(IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
return sb.toString();
}
private class TestUnit {
private final String WRONGPATH = "/Users/HelloKitty/hello.java";
private final String RIGHTPATH = "/Users/Wei/java/com/ciaoshen/thinkinjava/chapter11/MyReader.java";
private void testReadFile() {
System.out.println(readFile(RIGHTPATH));
System.out.println(readFile(WRONGPATH));
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
TestUnit test = new MyReader().new TestUnit();
test.testReadFile();
}
}
Exercise25.java
package com.ciaoshen.thinkinjava.chapter11;
import java.util.*;
import java.util.regex.*;
// statistics the word and their positions in the file
public class Exercise25 {
public static Map<String,ArrayList<Integer>> statistic(String path, String regex) {
if (path == null || regex == null) {
throw new RuntimeException("Argument content or regex is null!");
}
String content = new MyReader().readFile(path);
if (content == null) {
throw new RuntimeException("The content in " + path + " is null!");
}
Matcher matcher = Pattern.compile(regex).matcher(content);
Map<String,ArrayList<Integer>> result = new HashMap<String,ArrayList<Integer>>();
ArrayList<Integer> value = new ArrayList<Integer>();
String key = "";
while (matcher.find()) {
key = matcher.group();
if (result.containsKey(key)) {
value = result.get(key);
value.add(matcher.start());
result.put(key,value);
continue;
}
result.put(matcher.group(), new ArrayList<Integer>(Arrays.asList(matcher.start())));
}
return result;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String path = "/Users/Wei/java/com/ciaoshen/thinkinjava/chapter11/Exercise25.java";
String regex = "\\w+";
System.out.println(statistic(path,regex));
}
}
Exercise26.java
package com.ciaoshen.thinkinjava.chapter11;
import java.util.*;
public class Exercise26 {
public static LinkedHashMap<String,ArrayList<Integer>> sortedStatistic(String path, String regex) {
Map<String,ArrayList<Integer>> shuffleWordMap = Exercise25.statistic(path,regex);
Map<Integer,String> indexMap = getIndexMap(shuffleWordMap);
List<Map.Entry<Integer,String>> indexList = new ArrayList<Map.Entry<Integer,String>>();
indexList.addAll(indexMap.entrySet());
Collections.sort(indexList, new Comparator<Map.Entry<Integer,String>>() {
public int compare(Map.Entry<Integer,String> entry1, Map.Entry<Integer,String> entry2) {
return entry1.getKey().compareTo(entry2.getKey());
}
});
LinkedHashMap<String,ArrayList<Integer>> sortedWordMap = new LinkedHashMap<String,ArrayList<Integer>>();
for (Map.Entry<Integer,String> entry : indexList) {
String word = entry.getValue();
sortedWordMap.put(word,shuffleWordMap.get(word));
}
return sortedWordMap;
}
public static Map<Integer,String> getIndexMap(Map<String,ArrayList<Integer>> shuffleMap) {
Map<Integer,String> resultIndex = new HashMap<Integer,String>();
for (Map.Entry<String,ArrayList<Integer>> entry : shuffleMap.entrySet()) {
resultIndex.put(entry.getValue().get(0),entry.getKey());
}
return resultIndex;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String path = "/Users/Wei/java/com/ciaoshen/thinkinjava/chapter11/Exercise25.java";
String regex = "\\w+";
System.out.println(sortedStatistic(path,regex));
}
}
Exercise 27
- Exercise 27: (2) Write a class called Command that contains a String and has a method operation( ) that displays the String. Write a second class with a method that fills a Queue with Command objects and returns it. Pass the filled Queue to a method in a third class that consumes the objects in the Queue and calls their operation( ) methods.
package com.ciaoshen.thinkinjava.chapter11;
import java.util.*;
import java.lang.reflect.*;
public class Exercise27 {
private static enum LinuxCommand {
CD,LS,GREP,FIND,CP,MV,RM,PS,KILL,FILE,TAR,CAT;
public String toString() {
return name().toLowerCase();
}
public static LinuxCommand random() {
Random rand = new Random();
LinuxCommand[] values = LinuxCommand.class.getEnumConstants();
return values[rand.nextInt(values.length)];
}
}
public static class Command {
private static int count = 0;
private final int ID = ++count;
private final String COMMAND;
public Command(String str) {
COMMAND = str;
}
public void operation() {
System.out.println(this);
}
public String toString() {
return "Command#" + ID + ": " + COMMAND;
}
}
public static Queue<Command> fillCommandQueue(int size) {
Queue<Command> queue = new LinkedList<Command>();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
queue.add(new Command(LinuxCommand.random().toString()));
}
return queue;
}
public static void printCommands(Queue<Command> commands) {
for (Command command : commands) {
command.operation();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
//System.out.println(fillCommandQueue(20));
printCommands(fillCommandQueue(20));
}
}
Exercise 28
- Exercise 28: (2) Fill a PriorityQueue (using offer( )) with Double values created using java.util.Random, then remove the elements using poll( ) and display them.
package com.ciaoshen.thinkinjava.chapter11;
import java.util.*;
public class Exercise28 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Random rand = new Random();
PriorityQueue<Double> pq = new PriorityQueue<Double>();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
pq.offer(rand.nextDouble());
}
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
System.out.println(pq.poll());
}
}
}
Exercise 29
- Exercise 29: (2) Create a simple class that inherits from Object and contains no members, and show that you cannot successfully add multiple elements of that class to a PriorityQueue. This issue will be fully explained in the Containers in Depth chapter.
要么构造PriorityQueue的时候给一个Comparator。不然,PriorityQueue里的元素必须实现Comparable接口。
package com.ciaoshen.thinkinjava.chapter11;
import java.util.*;
public class Exercise29 {
private static class NoMemberClass extends Object {}
public static void main(String[] args) {
PriorityQueue<NoMemberClass> pq = new PriorityQueue<NoMemberClass>();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
pq.offer(new NoMemberClass());
}
}
}
####Exercise 30
- Exercise 30: (5) Modify CollectionSequence.java so that it does not inherit from AbstractCollection, but instead implements Collection.
Exercise30.java
package com.ciaoshen.thinkinjava.chapter11;
import java.util.*;
public class Exercise30 {
private static enum LinuxCommand {
CD,LS,GREP,FIND,CP,MV,RM,PS,KILL,FILE,TAR,CAT;
public String toString() {
return name().toLowerCase();
}
private static LinuxCommand random() {
Random rand = new Random();
LinuxCommand[] values = LinuxCommand.class.getEnumConstants();
return values[rand.nextInt(values.length)];
}
private static LinuxCommand[] randomProgram(int size) {
LinuxCommand[] program = new LinuxCommand[size];
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
program[i] = random();
}
return program;
}
}
public static class CommandSequence implements Collection<LinuxCommand> {
// object array
private LinuxCommand[] program;
private int cursor = 0;
public CommandSequence(int size) {
program = LinuxCommand.randomProgram(size);
}
public boolean add(LinuxCommand c) { //数组如果满了,循环从头插入
if (c == null) {
return false;
}
program[cursor++] = c;
if (cursor == program.length) {
cursor = 0;
}
return true;
}
public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends LinuxCommand> c) {
if (c == null || c.isEmpty()) {
return false;
}
for (LinuxCommand command : c) {
if (!add(command)) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
public void clear() {
program = new LinuxCommand[program.length];
}
public boolean contains(Object o) {
LinuxCommand c = (LinuxCommand)o;
for (LinuxCommand ele : program) {
if (ele == c) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
public boolean containsAll(Collection<?> c) {
if (c == null || c.isEmpty()) {
return false;
}
for (Object o : c) {
if (! contains(o)) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return size() == 0;
}
public boolean remove(Object o) {
if (!(o instanceof LinuxCommand)) {
return false;
}
for (int i = 0; i < program.length; i++) {
if (program[i] == (LinuxCommand)o) {
program[i] = null;
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
public boolean removeAll(Collection<?> c) {
boolean changed = false;
if (c == null || c.isEmpty()) {
return changed;
}
for (Object o : c) {
if (remove(o)) {
changed = true;
}
}
return changed;
}
public boolean retainAll(Collection<?> c) {
boolean changed = false;
if (c == null || c.isEmpty()) {
return changed;
}
for (Object o : this) {
if (!c.contains(o)) {
if(remove(o)) {
changed = true;
}
}
}
return changed;
}
public Object[] toArray() {
Object[] result = new Object[program.length];
for (int i = 0; i < program.length; i++) {
result[i] = program[i];
}
return result;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public <T> T[] toArray(T[] array) {
Object[] result = new Object[program.length];
for (int i = 0; i < program.length; i++) {
result[i] = program[i];
}
return (T[])result;
}
public int size() { return program.length; }
public Iterator<LinuxCommand> iterator() {
return new Iterator<LinuxCommand>() {
private int index = 0;
public boolean hasNext() {
return index < program.length;
}
public LinuxCommand next() { return program[index++]; }
public void remove() { // Not implemented
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
};
}
}
public static class InterfaceVsIterator {
public static <T> void display(Collection<T> c) {
for (T ele : c) {
System.out.println(ele);
}
}
public static <T> void display(Iterator<T> ite) {
while (ite.hasNext()) {
System.out.println(ite.next());
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
CommandSequence c = new CommandSequence(10);
InterfaceVsIterator.display(c);
InterfaceVsIterator.display(c.iterator());
}
}
Exercise30V2.java
也有个偷懒的办法,只写一个Iterator类和iterator()方法。其他用不到方法都抛出UnsupportedOperationException。
package com.ciaoshen.thinkinjava.chapter11;
import java.util.*;
public class Exercise30V2 {
private static enum LinuxCommand {
CD,LS,GREP,FIND,CP,MV,RM,PS,KILL,FILE,TAR,CAT;
public String toString() {
return name().toLowerCase();
}
private static LinuxCommand random() {
Random rand = new Random();
LinuxCommand[] values = LinuxCommand.class.getEnumConstants();
return values[rand.nextInt(values.length)];
}
private static LinuxCommand[] randomProgram(int size) {
LinuxCommand[] program = new LinuxCommand[size];
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
program[i] = random();
}
return program;
}
}
public static class CommandSequence implements Collection<LinuxCommand> {
// object array
private LinuxCommand[] program;
private int cursor = 0; //current pointer
public CommandSequence(int size) {
program = LinuxCommand.randomProgram(size);
}
public boolean add(LinuxCommand c) { //数组如果满了,循环从头插入
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends LinuxCommand> c) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
public void clear() {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
public boolean contains(Object o) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
public boolean containsAll(Collection<?> c) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
public boolean remove(Object o) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
public boolean removeAll(Collection<?> c) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
public boolean retainAll(Collection<?> c) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
public Object[] toArray() {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
public <T> T[] toArray(T[] array) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
public int size() {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
public Iterator<LinuxCommand> iterator() {
return new Iterator<LinuxCommand>() {
private int index = 0;
public boolean hasNext() {
return index < program.length;
}
public LinuxCommand next() { return program[index++]; }
public void remove() { // Not implemented
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
};
}
}
public static class InterfaceVsIterator {
public static <T> void display(Collection<T> c) {
for (T ele : c) {
System.out.println(ele);
}
}
public static <T> void display(Iterator<T> ite) {
while (ite.hasNext()) {
System.out.println(ite.next());
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
CommandSequence c = new CommandSequence(10);
InterfaceVsIterator.display(c);
InterfaceVsIterator.display(c.iterator());
}
}
Exercise 31
- Exercise 31: (3) Modify polymorphism/shape/RandomShapeGenerator.java to make it Iterable. You’ll need to add a constructor that takes the number of elements that you want the iterator to produce before stopping. Verify that it works.
package com.ciaoshen.thinkinjava.chapter11;
import java.util.*;
public class Exercise31 {
public static class Shape {
public void draw() {}
public void erase() {}
}
public static class Circle extends Shape {
public void draw() { System.out.println("Circle.draw()"); }
public void erase() { System.out.println("Circle.erase()"); }
}
public static class Square extends Shape {
public void draw() { System.out.println("Square.draw()"); }
public void erase() { System.out.println("Square.erase()"); }
}
public static class Triangle extends Shape {
public void draw() { System.out.println("Triangle.draw()"); }
public void erase() { System.out.println("Triangle.erase()"); }
}
public static class RandomShapeGenerator implements Iterable<Shape> {
private Random rand = new Random();
private final int size;
public RandomShapeGenerator(int num) {
size = num;
}
public Iterator<Shape> iterator() {
return new Iterator<Shape>() {
private int index = 0;
public boolean hasNext() {
return index < size;
}
public Shape next() {
index++;
switch(rand.nextInt(3)) {
default:
case 0: return new Circle();
case 1: return new Square();
case 2: return new Triangle();
}
}
};
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int shapeNum = 10;
RandomShapeGenerator gen = new RandomShapeGenerator(shapeNum);
for (Shape s : gen) {
s.draw();
}
}
}
Exercise 32
- Exercise 32: (2) Following the example of MultilterableClass, add reversed( ) and randomized( ) methods to NonCollectionSequence.java, as well as making NonCollectionSequence implement Iterable, and show that all the approaches work in foreach statements.
LinuxCommand.java
package com.ciaoshen.thinkinjava.chapter11;
import java.util.*;
public enum LinuxCommand {
CD,LS,GREP,FIND,CP,MV,RM,PS,KILL,FILE,TAR,CAT;
public String toString() {
int id = ordinal() + 1;
String name = name().toLowerCase();
return "Command#" + id + ": " + name;
}
public static LinuxCommand random() {
Random rand = new Random();
LinuxCommand[] values = LinuxCommand.class.getEnumConstants();
return values[rand.nextInt(values.length)];
}
public static LinuxCommand orderGet(int index) {
LinuxCommand[] values = LinuxCommand.class.getEnumConstants();
return values[(index % values.length)];
}
public static LinuxCommand[] randomProgram(int size) {
LinuxCommand[] program = new LinuxCommand[size];
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
program[i] = random();
}
return program;
}
public static LinuxCommand[] orderProgram(int size) {
LinuxCommand[] program = new LinuxCommand[size];
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
program[i] = orderGet(i);
}
return program;
}
}
Exercise32.java
package com.ciaoshen.thinkinjava.chapter11;
import java.util.*;
public class Exercise32 {
public static class CommandSequence {
protected final LinuxCommand[] commands;
public CommandSequence(int size) {
commands = LinuxCommand.orderProgram(size);
}
}
public static class NonCollectionCommandSequence extends CommandSequence implements Iterable<LinuxCommand> {
public NonCollectionCommandSequence(int size) {
super(size);
}
public Iterator<LinuxCommand> iterator() {
return new Iterator<LinuxCommand>() {
private int index = 0;
public boolean hasNext() {
return index < commands.length;
}
public LinuxCommand next() {
return commands[index++];
}
};
}
}
public static class MultiIterableCommandSequence extends NonCollectionCommandSequence {
public MultiIterableCommandSequence(int size) {
super(size);
}
public Iterable<LinuxCommand> reverse() {
return new Iterable<LinuxCommand>() {
public Iterator<LinuxCommand> iterator() {
return new Iterator<LinuxCommand>() {
private int index = commands.length-1; //begin from the last element
public boolean hasNext() {
return index >= 0;
}
public LinuxCommand next() {
return commands[index--];
}
};
}
};
}
public Iterable<LinuxCommand> shuffle() {
return new Iterable<LinuxCommand>() {
public Iterator<LinuxCommand> iterator() {
ArrayList<LinuxCommand> commandsCopyList = new ArrayList<LinuxCommand>(Arrays.asList(commands));
Collections.shuffle(commandsCopyList);
return commandsCopyList.iterator();
}
};
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MultiIterableCommandSequence commands = new MultiIterableCommandSequence(10);
System.out.println("NORMAL ORDER >>>");
for (LinuxCommand command : commands) {
System.out.println(command);
}
System.out.println("REVERSE ORDER >>>");
for (LinuxCommand command : commands.reverse()) {
System.out.println(command);
}
System.out.println("SHUFFLE ORDER >>>");
for (LinuxCommand command : commands.shuffle()) {
System.out.println(command);
}
}
}